
Tokushima ASNPs (Asian SNPs) HOMEPAGE
You are the






 visitor since Apr 7, 2003.
visitor since Apr 7, 2003.
Allele Frequency Database in Asians including Japanese and Chinese:
To make Gene-Centric Even-Spacing Common SNPs Probes available for High
Efficiency Case-Control Association Study:
[updated on August 27, 2005]
Tokushima ASNPs ―Brief Summary―
|
| A Total Number of SNPs examined |
91,276 |
| A Total Number of SNPs with Minor Allele Frequency >=
0.15 in Japanese |
70,099 |
| A Total Number of SNPs with Minor Allele Frequency >=
0.15 in Chinese |
69,161 |
[SNPs table]
Chr. 1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
X Y
Genome Science is directing from "Structural Genomics"
to "Functional Genomics". After the publication of a rough draft
of human genome sequence in 2000, the human genome sequence has recently
completed on April 14, 2003. The genome research has got into the Post-Sequence
(Post-Genome) era. Enormous efforts are being poured to find the polymorphisms
to determine various phenotypes based on the "case-control association
studies". Owing to the discovery of millions of SNPs (Single Nucleotide
Polymorphisms) by the world-wide efforts, the search for the disease
susceptibility genes or drug response-determining genes and their polymorphisms
has now become feasible for multi-factorial "common diseases".
The susceptibility genes for "common diseases" including diabetes, rheumatoid
arthritis, gout, schizophrenia, cancers etc are now being intensely searched. SNPs have
given the researchers the completely new concept and tool to find the
association between individual genotypes with various phenotypes. The
discovery of the genetic basis for individual differences will open the
genome-information based drug
discovery, genetic diagnosis, and individualized medicine.
In case of diabetes as the representative multi-factorial disease,
the increasing number of diabetes in Japan is threatening the medical cost and the
society. The number of diabetic patients now reached about 7 million
patients and 7 millions of those with impaired glucose tolerance making a total
number of 14 millions with a threat of diabetes. This is similar to the
epidemic increasing tendency in a total number of 150 million diabetic patients in the
whole world. The increase of patients with severe diabetic
complications in Japan is reflected by the fact that 3,000 diabetic patients
newly become
blind per year and that 12,000 diabetic patients are introduced to hemodialysis every year in
Japan.
It is thus critically important to establish the
high-efficiency methods for association study to find disease susceptibility
genes and their responsible SNPs or haplotypes. We have found that
"Even-Spacing Common SNPs Probes" affords researchers the most
efficient way of finding disease susceptibility genes.
We hope to contribute to the discovery of disease
susceptibility genes and the development of genome information- based medicine
by establishing Gene-Centric Even-Spacing Common SNPs Probes.
Tokushima ASNPs (Asian SNPs)
Database named
"Tokushima ASNPs"
supplies minor allele frequencies of Gene-Centric Even-Spacing Common
SNPs in Japanese and Chinese. These Minor Allele Frequency data can be
used to select the most efficient SNP probes for the high-efficiency Case-Control
association study.
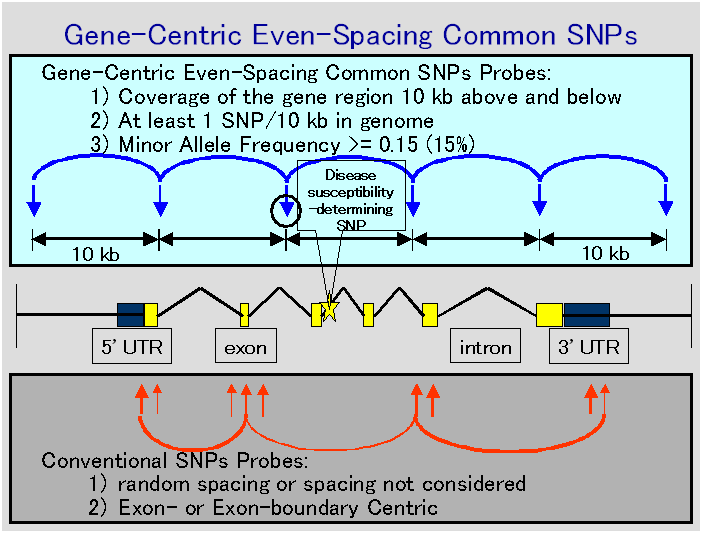
The concepts of Gene-Centric Even-Spacing Common SNPs are examined
in the figure below. The idea of "Gene-Centric" means the gene region spanning 10 kb
above the start of an open reading frame and 10 kb below the stop codon. The
idea of "Common SNPs" means the Minor Allele Frequency >= 15% in
45 healthy
Japanese or Chinese subjects. The purpose of this database is finally to make
"Gene-Centric Even-spacing Common Shared SNPs probes" available for
association study in Japanese and Chinese. The total number of SNPs reached more than
900,000.
The results of the analysis on the number of SNPs
showing the minor allele frequency larger than 15% en each chromosme are
summarized in the following Table. This table shows the results in 4
different populations including Caucasian, African American, Chinese, and
Japanese.
| Chromosome |
A Total
Number of SNPs |
A
Total Number of SNPs with Minor Allele Frequency >= 0.15 in Caucasian
(percentage) |
A
Total Number of SNPs with Minor Allele Frequency >= 0.15 in African
American (percentage) |
A
Total Number of SNPs with Minor Allele Frequency >= 0.15 in Chinese
(percentage) |
A Total Number of SNPs with Minor Allele
Frequency >= 0.15 in Japanese (percentage) |
| 1 |
6,542 |
4,462 |
(68%) |
4,201 |
(64%) |
5,009 |
(77%) |
4,997 |
(76%) |
| 2 |
6,179 |
4,278 |
(69%) |
4,034 |
(65%) |
4,639 |
(75%) |
4,736 |
(77%) |
| 3 |
6,035 |
4,294 |
(71%) |
4,019 |
(67%) |
4,461 |
(74%) |
4,456 |
(74%) |
| 4 |
4,169 |
2,922 |
(70%) |
2,685 |
(64%) |
3,176 |
(76%) |
3,223 |
(77%) |
| 5 |
4,364 |
3,025 |
(69%) |
2,805 |
(64%) |
3,379 |
(77%) |
3,367 |
(77%) |
| 6 |
10,531 |
6,826 |
(65%) |
6,343 |
(60%) |
7,905 |
(75%) |
8,114 |
(77%) |
| 7 |
4,865 |
3,384 |
(70%) |
3,149 |
(65%) |
3,679 |
(76%) |
3,698 |
(76%) |
| 8 |
3,702 |
2,703 |
(73%) |
2,456 |
(66%) |
2,849 |
(77%) |
2,927 |
(79%) |
| 9 |
3,447 |
2,455 |
(71%) |
2,293 |
(67%) |
2,629 |
(76%) |
2,665 |
(77%) |
| 10 |
4,121 |
2,906 |
(71%) |
2,642 |
(64%) |
3,109 |
(75%) |
3,173 |
(77%) |
| 11 |
4,433 |
3,181 |
(72%) |
2,951 |
(67%) |
3,447 |
(78%) |
3,526 |
(80%) |
| 12 |
4,396 |
2,946 |
(67%) |
2,688 |
(61%) |
3,235 |
(74%) |
3,309 |
(75%) |
| 13 |
2,257 |
1,629 |
(72%) |
1,501 |
(67%) |
1,818 |
(81%) |
1,784 |
(79%) |
| 14 |
2,792 |
1,907 |
(68%) |
1,776 |
(64%) |
2,124 |
(76%) |
2,191 |
(78%) |
| 15 |
2,610 |
1,800 |
(69%) |
1,689 |
(65%) |
1,968 |
(75%) |
1,986 |
(76%) |
| 16 |
2,251 |
1,430 |
(64%) |
1,348 |
(60%) |
1,636 |
(73%) |
1,689 |
(75%) |
| 17 |
2,867 |
1,829 |
(64%) |
1,756 |
(61%) |
2,165 |
(76%) |
2,221 |
(77%) |
| 18 |
1,909 |
1,307 |
(68%) |
1,311 |
(69%) |
1,446 |
(76%) |
1,482 |
(78%) |
| 19 |
2,349 |
1,528 |
(65%) |
1,428 |
(61%) |
1,774 |
(76%) |
1,784 |
(76%) |
| 20 |
3,514 |
2,636 |
(75%) |
2,493 |
(71%) |
2,727 |
(78%) |
2,742 |
(78%) |
| 21 |
3,314 |
2,309 |
(70%) |
2,109 |
(64%) |
2,580 |
(78%) |
2,619 |
(79%) |
| 22 |
3,188 |
2,152 |
(68%) |
1,920 |
(60%) |
2,340 |
(73%) |
2,364 |
(74%) |
| X |
1,433 |
918 |
(64%) |
883 |
(62%) |
1,059 |
(74%) |
1,038 |
(72%) |
| Y |
8 |
2 |
(25%) |
2 |
(25%) |
7 |
(88%) |
8 |
(100%) |
| Total |
91,276
|
62,829
|
(69%) |
58,482
|
(64%) |
69,161 |
(76%) |
70,099 |
(77%) |
Disclaimer and Liability
Institute for Genome Research The University of Tokushima make no representations or
warranties regarding the content or accuracy of the information and also
make no represents or warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose and
accept no responsibility for any consequences of the receipt or use of the information.
Div. Genetic Information ( )
)
Institute for Genome Research The University of Tokushima ( )
)
Last updated: 09-08-08
Institute for Genome Research, The University of Tokushima. All Rights Reserved.

visitor since Apr 7, 2003.


![]() )
)![]() )
)